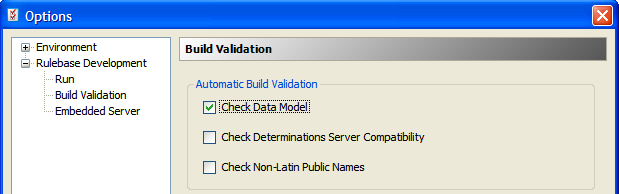
The validation will now be performed when the rulebase is built.
Once you have created the external data model, you can check that every base level attribute in the project has an attribute with the same ID, data type and entity level in the external data model. Validating against the data model will also check to ensure all base attributes have public names, thus ensuring attribute IDs are reliable and static. Applying data model constraints are turned off by default.
Check the rulebase against an external data model
Create an external data model file for use with Oracle Policy Modeling
To check the rulebase against an external data model:

NOTE: The validation
setting is a user-specific setting and will need to be performed on every
developer's machine.
An external data model file can either be created by Oracle Policy Modeling or it can be created elsewhere.
Creating the data model file from within Oracle Policy Modeling requires having a rulebase which already reflects the desired data model. This means creating all the entities and attributes you need in a blank new project or, if the rules are already quite well progressed, making sure the rulebase you are working with already has the desired data model. You then export the data model to XML in the usual way, to create an external data file that you can use with Oracle Policy Modeling.
If the data model is not created by Oracle Policy Modeling, then the file needs to be transformed into the correct format. See Oracle Policy Automation Developer's Guide for more information.
The Data Model view in Oracle Policy Modeling shows the rulebase data model.
To open the Data Model view select View | Data Model. The Data Model view will open in the top right hand pane of Oracle Policy Modeling.
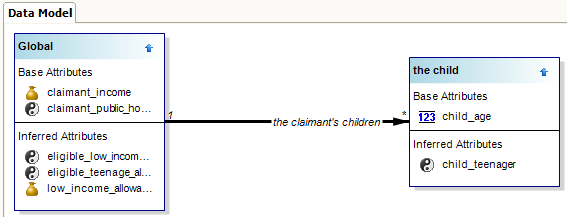
Each entity in the rulebase is displayed as a separate box with base-level and inferred attributes belonging to that entity displayed in the box. Relationships between entities are shown as connectors between the entity boxes.